The Powerful Benefits Of Garlic For Skin Health
by Alec Carloss February 06, 2023

Garlic, scientifically known as Allium sativum, is an ancient herb that has been used for centuries for its medicinal properties. Its use can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as Greece, where it was used by the Olympians as one of the earliest performance enhancing substances on record.
The ancient Greeks believed that consuming garlic before athletic competitions would give them the strength and endurance they needed to perform at their best.
Garlic was also presumed to have been used by the ancient Greeks as a medicinal herb to treat a variety of ailments. The Greek physician, Hippocrates, who is known as the "Father of Medicine," wrote about the medicinal properties of garlic and recommended it for the treatment for several conditions, including respiratory and digestive problems, fighting infections, and maintaining a healthy life. "For those desiring to keep their health, let them eat garlic," Hippocrates said.
It wasn't just the mighty Greeks that had a long history with the benefits of garlic, as ancient Egyptians, Romans and Chinese also have used garlic for medicinal purposes.
The Chinese would consume it as a preventative measure against potential disease as they believed (correctly) that garlic could increase longevity, improve blood flow, and detoxify the body. Similar to the Greeks, the Romans consumed garlic as an energy and stamina booster before going to battle.
And the Egyptians used garlic not only for medicinal purposes but also for cosmetic reasons. They found garlic to be a useful substance for improving the appearance of their skin as it improved the texture and tone that gave the skin a more youthful glow.
Why is Garlic Such a Powerful Ingredient For Human Health?

Garlic is an extraordinarily rich source of organosulfur compounds (natural compounds that contain sulfur). The primary organosulfur compound found in garlic that is responsible for the majority of medicinal attributes is called allicin.
Allicin is formed through a process known as enzymatic conversion. When garlic is crushed, chopped, or chewed, an enzyme called alliinase comes into contact with alliin (S-allylcysteine sulfoxide) is then converted to allicin. Allicin is a highly reactive compound that quickly breaks down into other compounds (1).
It is hypothesized that allicin enables a complex yet effective delivery of bioavailable sulfur to the necessary pathways in the body which allow for a cascade of positive biological actions (2).
Labeling sulfur as the key is still to be determined. However, the scientific literature on the effects of allicin is undeniable with numerous studies demonstrating a host of health benefits.
Garlic Benefits for Skin
-
Anti-inflammatory
-
Antibacterial
-
Antioxidant
-
Anti cancer
-
Enhances Blood Flow and Improves Circulation
Anti-inflammatory Properties of Garlic
Garlic has profound anti inflammatory effects on the skin and other tissue of the human body.
One study, published in the Journal of Nutrition in 2019, looked at the effects of a garlic supplement that contained allicin on the levels of inflammatory markers in healthy adults.
The study found that the supplement significantly reduced the levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), which is another marker of inflammation, and also reduced the levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6), which is another marker of inflammation, compared to the placebo group (3).
A study published in the journal of Nutrition in 2008, looked at the effects of allicin supplements on elderly individuals with metabolic syndrome.
This study found that allicin supplementation significantly reduced the levels of CRP and IL-6, as well as other markers of inflammation, such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta) in the blood (4).
Another study, published in the Journal of Medicinal Food in 2002, investigated the effects of garlic supplements on patients with rheumatoid arthritis, which is an autoimmune disorder characterized by chronic inflammation.
The research found that the garlic supplement significantly reduced inflammation, as measured by the levels of C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate, which are markers of inflammation.
Antibacterial Benefits of Garlic
Garlic has been shown to have the capacity to kill harmful bacteria and fight bacterial infections.
A study published in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy in 2001 looked at the effects of garlic extract on a number of different bacterial species. The study found that garlic extract had strong antibacterial activity against several species of bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The study also found that the antibacterial activity of garlic extract was due, in part, to the presence of the compound allicin (5).
Another study, published in the Journal of Medicinal Food in 2002, looked at the effects of garlic extract on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), a type of bacteria that is resistant to many antibiotics. The study found that garlic extract was able to inhibit the growth of MRSA (6).
Garlic as an Antioxidant
Allicin, the organosulfur compound found in garlic has been linked to the production of glutathione, a powerful antioxidant found in the human body.
Published in the Journal of Nutrition in 2001, a study investigated the effects of garlic extract on the levels of glutathione in healthy adults. The study found that consuming garlic significantly increased the levels of glutathione in the blood, and that this increase was associated with a reduction in oxidative stress.
The study also found that garlic supplementation also increased the activity of enzymes involved in the synthesis of glutathione, such as glutathione synthetase and glutamate cysteine ligase (7).
More research published in the Journal of Food Science and Technology in 2020, investigated the effect of garlic on the levels of glutathione in the blood and liver of diabetic rats. The study found that garlic supplementation significantly increased the levels of glutathione in the blood and liver and also reduced the levels of oxidative stress markers.
The Link Between Garlic and Skin Health
The health benefits for the skin from the compounds contained in garlic are numerous as many of the compounds, and their respective properties, contribute in a variety of ways to the overall condition of the skin. The two most prominent physiological actions that garlic induces which significantly benefit the skin are: enhancing blood flow and increasing antioxidant levels in the body.
Reducing Blood Pressure
Garlic is a known vasodilator (widens the blood vessels) that significantly improves circulation in the human body.
Improving circulation can lead to healthier skin in several ways. The skin is the largest organ in the body and is supplied with blood through a network of blood vessels.
Good circulation ensures that the skin cells receive an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients. Oxygen is needed for the cells to produce energy through the process of cellular respiration, while a variety of nutrients in the form of vitamins and minerals are necessary for the cells to function properly.
When blood flow to the skin is poor, the skin cells may not receive enough oxygen and nutrients which lead to the skin appearing dull, pale, or lifeless. In addition, poor circulation can also lead to the accumulation of waste products in the skin, which can contribute to skin problems such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis.
Another mechanism influenced by improved blood flow is collagen synthesis. Collagen is a protein that makes up a significant portion of the skin and is responsible for giving it its structure and strength.
This process is complex and involves the activation of fibroblasts. Fibroblasts are cells found in connective tissue that produce collagen and other extracellular matrix components.
When fibroblasts are supplied with adequate oxygen, the process of collagen synthesis proceeds optimally, and new collagen fibers are produced. Collagen fibers are produced by the fibroblasts and are made up of collagen protein molecules. These fibers are then deposited into the extracellular matrix, where they provide strength and support to the skin.
Increase Antioxidant Levels
As discussed earlier, garlic acts as an antioxidant as well as a precursor to other antioxidant compounds such as glutathione. Antioxidants are substances capable of neutralizing harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS), also known as free radicals, which can naturally be produced in the body during normal metabolic processes. These free radicals have been linked to various skin disorders such as photoaging, hyperpigmentation, and skin cancer.
The skin is exposed to a variety of environmental factors such as UV radiation, pollution, and smoke. These can lead to an increase in the levels of free radicals in the skin which are capable of causing damage to the DNA, proteins, and lipids of the skin cells, leading to inflammation, cell death, and ultimately skin aging.
Antioxidants, such as the compounds found in garlic, neutralize free radicals by donating an electron to stabilize them. This action prevents the free radicals from causing further damage to the skin cells. The benefits of garlic as an antioxidant also help to prevent the formation of new free radicals, thus providing a protective barrier against environmental damage.
Garlic Derived Organosulfur Compounds
It is important to list and discuss some of the other bioactive compounds that add to the benefits of garlic. There are a variety of compounds contained within garlic that give it such powerful medicinal properties that improve the skin and overall health. Some of the most well-known garlic compounds include:
Allicin:
As mentioned earlier but worth noting again, allicin is the most powerful substance found in garlic. This is a sulfur-containing compound that is responsible for the characteristics odor of garlic. It has been shown to have antimicrobial properties, meaning it can inhibit the growth of bacteria, viruses, and fungi. It also has antioxidant properties,, meaning it can neutralize harmful free radicals that can damage cells. It also has anti-inflammatory properties that aid in reducing inflammation in the skin and other parts of the body.
S-allylcysteine:
This is a compound that is similar in structure to allicin and is believed to have similar medicinal properties. It is found in garlic in higher concentrations than allicin. It has been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and to be beneficial for cardiovascular health.
Diallyl disulfide (DADS):
This is another sulfur-containing compound found in garlic that has antimicrobial, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. It has been shown to have a preventive effect on certain types of cancer, particularly lung cancer.
Alliin:
This is a compound that is present in garlic in its raw form and is converted into allicin when garlic is crushed or chopped. It hasn't been studied as thoroughly as the other compounds but shows a kinship to allicin in health benefits.
Alliinase:
This is an enzyme that is responsible for converting alliin into allicin
Gamma-glutamylcysteines:
These are also sulfur-containing compounds that are found in garlic that have been linked to lowering cholesterol.
Flavonoids:
These are a large class of phytochemicals (naturally occurring chemicals found in plants) that are known for their antioxidant properties. Garlic contains flavonoids like quercetin, kaempferol, and saponins which have been shown in studies to hinder the aging process and provide relief to other skin conditions.
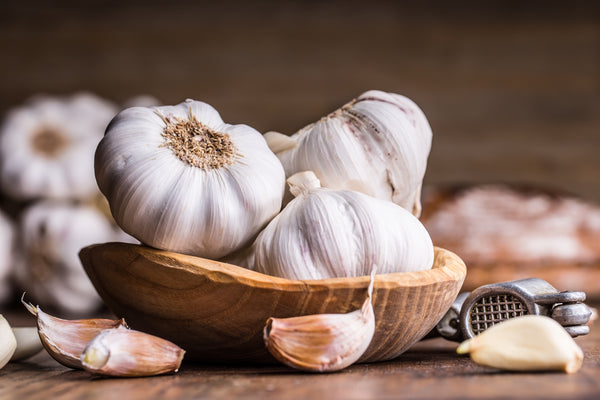
Best ways to Receive the Benefits of Garlic

-
Eating raw garlic:
One of the most effective ways to consume garlic is to eat it raw. Crushed garlic cloves (as mentioned earlier) releases an enzyme called alliinase, which converts the compound alliin into allicin. Eating raw garlic cloves or adding raw garlic cloves to salads, sandwiches or dips can provide you with a decent dose of allicin. If you are truly brave, you can also blend a garlic mixture with water to make raw garlic juice. However, many people find the taste of raw garlic cloves too strong and pungent. It requires some adaptation to eat raw garlic.
-
Garlic Supplements:
Garlic supplements are another way to consume garlic and receive the health benefits for the skin. Allium sativum (garlic) supplements are available in different forms such as capsules, tablets, and oils. Supplements that combine garlic with other skin enhancing ingredients are also an optimal way to receive and magnify the positive effects of garlic.
-
Cooking Garlic:
Cooking garlic cloves can also provide some benefits to the skin and other health benefits, although the allicin content will be substantially reduced from the high heat. When garlic cloves are cooked, it releases other beneficial compounds such as diallyl disulfide and diallyl trisulfide, which have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Dietary Garlic can be added and used as a base ingredient to countless dishes such as soups, stews, and pasta sauces.
-
Garlic Oil:
Garlic Oil is made by infusing crushed garlic or garlic extract in a carrier oil such as olive oil. Garlic oil can be used as a dietary supplement or as a topical treatment for skin conditions. Garlic oil can be applied topically to the skin for skin smoothing benefits, removing dead skin cells, and to reduce inflammation and prevent infection.
Recap
"Let food be thy medicine, and medicine be thy food." The words of Hippocrates ring true and hold the secret to maintaining healthy skin and a healthy life. The benefits of garlic are rich and abundant. Remind yourself daily of the power of garlic as a potent substance to elevate the health of your skin. Eat it fresh, eat it encapsulated, and eat it often.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How much Garlic should I consume to receive the beneficial effects of garlic?
The recommended daily intake of garlic varies depending on the source. A general guideline is to consume at least the equivalent of 2-4 fresh cloves per day or 400-1200 of garlic extract in supplement form per day.
Can I use Garlic supplements if I am taking blood-thinning medications?
Garlic supplements may interact with blood-thinning medications such as warfarin, and may increase the risk of bleeding. It's a good idea to consult with your prescribing physician if you are on medications for high blood pressure before taking garlic supplements.
Is Fresh Garlic more effective than garlic supplements?
Fresh garlic is considered more effective as it releases allicin, which is responsible for the majority of garlic's skin benefits. Eating or drinking raw garlic will give you a healthy and potent dose of allicin, but most people would consider that method uncomfortable. Supplements can still do the job effectively.
Can Garlic Be Used for treating acne?
Some research suggests that garlic may have potential benefits in treating acne. A study published in the Journal of Dermatological Science in 2018 found that garlic extract significantly decreased the level of oxidative stress markers in the skin, as well as the production of inflammatory cytokines. Garlic also reduces inflammation from skin irritation that can lead to acne. In this case, garlics ability to reduce acne may be useful with beauty benefits.
Also in EN-1 Blog

Turmeric and Ginger Benefits
by Alec Carloss February 08, 2023

Skin Care For Men: What You Need To Know
by Alec Carloss February 06, 2023

Why Hyaluronic Acid Supplements Should be Part of Your Skin Care Routine
by Alec Carloss January 23, 2023
Hyaluronic acid is a molecule with a variety of important functions in the body. It has shown to have remarkable benefits for the skin and joints as an oral supplement. Adding hyaluronic acid supplements to your skin care routine may be a highly effective method to improving your skin health. Find the best hyaluronic acid supplements here.
SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER
Join our community and learn how you can improve your health and live a longer, more fulfilling life!
© 2025 EN-1


Alec Carloss
Author